NCERT Science Class 9 Chapter 5 Question Answer Solutions – THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE FREE PDF Download 2025-26
Page – 51
🔍 Q. 1. Who discovered cells, and how? ✨
➡️Answer:-
🔬 Discovery of Cells
👉 Discovered by: Robert Hooke (1665)
🧐 How was it discovered?
Robert Hooke, an English scientist, observed a thin slice of cork (bark of a tree) under a self-designed microscope. He noticed small, box-like structures which he called “cells”, as they resembled the tiny rooms in a monastery, known as cells.
📜 Importance of Hooke’s Discovery:
Although Hooke could only observe dead plant cells, his discovery laid the foundation for cell theory, which later established that all living organisms are made up of cells.
✨ Fun Fact:
The term “cell” comes from the Latin word “cellula”, meaning a small room! 🏠
💡 Conclusion:
Robert Hooke was the first scientist to discover cells in 1665 while examining a cork slice under a microscope, paving the way for modern biology! 🌱🔍
Q. 2. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer:-
🧬 Why is the Cell Called the Structural and Functional Unit of Life?
🔹 🔗 Structural Unit:
Cells are the building blocks of all living organisms. Just like bricks form a house 🏠, cells come together to form tissues, organs, and entire organisms.
🔹 ⚙ Functional Unit:
Cells carry out all essential life processes such as respiration 🌬, digestion 🍽, excretion 🚮, and reproduction 🍼. Each cell works like a tiny factory ensuring survival.
🔹 ✨ Key Points:
✅ Every living organism is made up of cells.
✅ Cells perform all necessary biological activities.
✅ Specialized cells form different tissues, organs, and systems.
💡 Conclusion:
Cells are called the structural and functional units of life because they form the basic structure of living organisms and carry out all vital functions required for survival! 🌿🔬
Page – 53
Q. 1. How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer:-
🌱 Movement of Substances Like CO₂ and Water In and Out of the Cell
🔹 1. Diffusion 🚶♂️
- CO₂ and O₂ move in and out of the cell through diffusion.
- Diffusion is the process where molecules move from a higher concentration to a lower concentration until equilibrium is reached.
- Example: Cells produce CO₂ as a waste product. Since the concentration of CO₂ is higher inside the cell, it moves out into the surroundings. Conversely, O₂ enters the cell from the surroundings as its concentration is higher outside.
🔹 2. Osmosis 💧
- Water moves in and out of the cell through osmosis, a special type of diffusion for water molecules.
- Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
- Example: If a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution (low solute, high water), water enters the cell, causing it to swell. If placed in a hypertonic solution (high solute, low water), water moves out, causing the cell to shrink.
💡 Conclusion:
CO₂ and O₂ move by diffusion while water moves by osmosis, both processes ensuring the exchange of essential substances for cellular survival! 🌿🔬
Q. 2. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer:-
🧪 Why is the Plasma Membrane Called a Selectively Permeable Membrane?
🔹 🔬 Definition:
The plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane because it allows only certain substances to enter or exit the cell while blocking others. 🚪✨
🔹 ⚙ How Does It Work?
The plasma membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer 🏗 with embedded proteins 🧩. This unique structure helps in selective transport, meaning:
✅ Allows essential molecules like oxygen (O₂), water (H₂O), and nutrients to enter the cell.
❌ Restricts harmful substances and prevents the loss of vital components.
🔹 🛤 Methods of Transport:
1️⃣ Passive Transport (🚶♂️ No Energy Needed)
- Diffusion: Movement of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide (CO₂). 🌬
- Osmosis: Movement of water molecules. 💧
2️⃣ Active Transport (⚡ Requires Energy) - Transport of ions and large molecules against their concentration gradient. 🔄
💡 Conclusion:
Since the plasma membrane controls what enters and exits, it is selectively permeable, ensuring the cell’s safety and functionality! 🔬🌱
📖 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Use diagrams 🖼 to explain the concept clearly.
✅ Mention key transport processes like diffusion, osmosis, and active transport for better marks.
✅ Keep answers concise yet detailed for full marks! ✨📚
Page – 55
Q. 1. Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
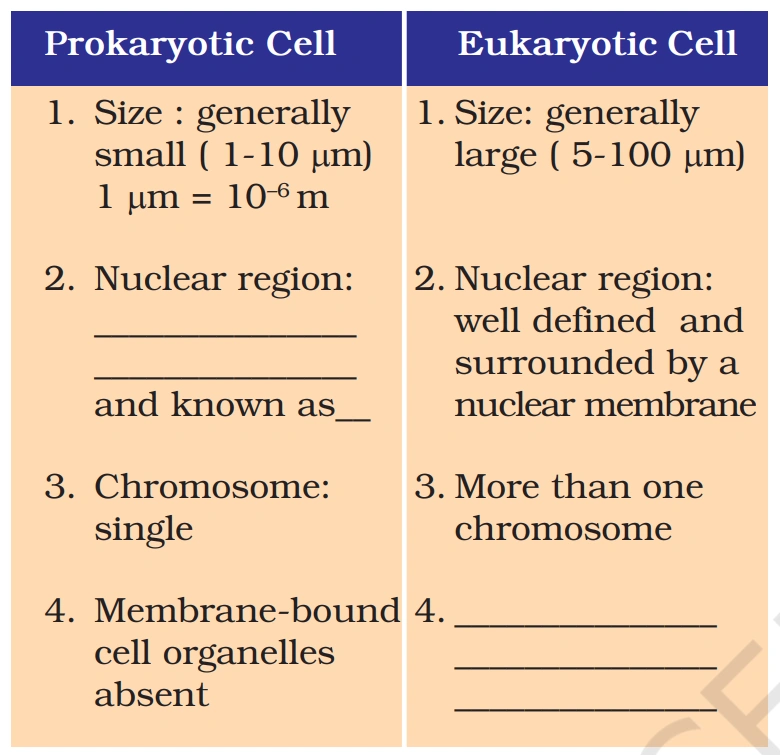
Answer:-
🔬 Filled-in Table: Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Here’s your completed table with the missing information:
| Feature 🏷️ | Prokaryotic Cell 🦠 | Eukaryotic Cell 🧬 |
|---|---|---|
| Size 📏 | Generally small (1-10 µm) | Generally large (5-100 µm) |
| Nuclear Region 🎯 | ❌ Not well defined because of the absense of nuclear membrance and known as nucleoid | ✅ Well-defined nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane |
| Chromosome Number 🧬 | Single | More than one |
| Membrane-bound Organelles 🏭 | ❌ Absent | ✅ Present (e.g., mitochondria, Golgi body, ER) |
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Use examples like bacteria (prokaryotic) and plants/animals (eukaryotic) for extra marks! 🌱
✅ Try drawing a simple diagram to make your answer visually appealing 🖼️.
✅ Keep your explanation concise yet detailed to maximize your score! 🎯
Page – 57
Q. 1. Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer:-
🧬 Organelles That Contain Their Own Genetic Material
🔹 1. Mitochondria ⚡
- Known as the “powerhouse of the cell”, mitochondria generate energy (ATP) through cellular respiration. 🔥
- It has its own DNA 🧬 and ribosomes, allowing it to replicate independently.
- Found in both plant and animal cells. 🌱🐾
🔹 2. Chloroplasts 🌿
- Present only in plant cells and some algae, chloroplasts help in photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy. ☀️
- It also contains its own DNA 🧬 and ribosomes, enabling self-replication like mitochondria.
- The green pigment chlorophyll inside chloroplasts captures sunlight. 🌞
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Mention both organelles and their functions for full marks.
✅ Highlight their ability to replicate independently due to their DNA & ribosomes. 🔬
✅ Use a neat diagram 🖼️ in your answer to make it visually appealing!
✅ Keep your explanation concise yet detailed for better clarity.
Q. 2. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer:-
⚠️ Effect of Cell Disorganization Due to Physical or Chemical Influence
🔹 🔬 Importance of Cell Organization:
Every living cell functions systematically due to its well-organized structure, where different organelles perform specific roles. 🏗️
🔹 🚨 Consequences of Cell Disorganization:
If a cell’s organization is disturbed due to physical or chemical damage, the following effects occur:
✅ Loss of Function ⚙️: Organelles like mitochondria, ribosomes, and the nucleus stop working, affecting cellular activities.
✅ Interruption in Metabolism 🔥: Essential processes like respiration, digestion, and waste removal are disrupted.
✅ Cell Death ☠️: If the damage is severe and irreversible, the cell loses its ability to survive and eventually dies.
🔹 ⚠️ Causes of Disorganization:
❌ Physical Influence: High temperature, mechanical injury, radiation.
❌ Chemical Influence: Toxic substances, strong acids/bases, harmful drugs.
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Mention how the loss of cell organization affects essential functions.
✅ Use examples of physical & chemical influences for clarity.
✅ If possible, include a diagram 🖼️ illustrating cell disintegration.
✅ Keep answers concise yet well-explained for full marks! ✅📚
Q. 3. Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer:-
🦠 Why Are Lysosomes Known as Suicide Bags?
🔹 🔬 What Are Lysosomes?
Lysosomes are small, membrane-bound organelles filled with digestive enzymes. They help break down waste, damaged organelles, and harmful substances inside the cell. 🚮🛠️
🔹 ☠️ Why ‘Suicide Bags’?
Lysosomes are called “suicide bags” because:
✅ Self-Destruction Mechanism: When a cell is damaged beyond repair, lysosomes burst, releasing their enzymes. This process leads to self-digestion of the cell. 🏗️➡⚡
✅ Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death): Lysosomes help in destroying old or unwanted cells, ensuring proper growth and maintenance of the organism. 🔄❌
🔹 🌟 Importance of Lysosomes:
✔ Help in digestion of cellular waste. 🚮
✔ Defend against pathogens (like bacteria). 🦠🛡️
✔ Play a vital role in cell renewal. 🌱✨
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Explain how lysosomes break down cellular components. 🛠️
✅ Mention apoptosis and self-digestion for full marks. ✨
✅ A neat diagram of a lysosome will make your answer stand out! 🖼️
✅ Keep your explanation concise but detailed for clarity. ✅📚
Q. 4. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer:-
🧬 Where Are Proteins Synthesized Inside the Cell?
🔹 💡 Key Organelles Involved:
✅ Ribosomes 🏭 – Known as the “protein factories” of the cell, ribosomes assemble amino acids into proteins.
✅ Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 🔬 – The rough ER (covered with ribosomes) helps in the processing and transportation of proteins.
✅ Cytoplasm 🌊 – Free ribosomes in the cytoplasm also synthesize proteins that remain within the cell.
🔹 ⚙ How Does Protein Synthesis Work?
1️⃣ Transcription 📝 – DNA is copied into mRNA inside the nucleus.
2️⃣ Translation ⚙️ – Ribosomes decode mRNA and assemble amino acids into proteins.
3️⃣ Processing & Transport 🚀 – The rough ER and Golgi apparatus modify and transport proteins to their destinations.
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Mention ribosomes as the primary site of protein synthesis for full marks.
✅ Briefly explain transcription and translation for clarity.
✅ Draw a simple diagram 🖼️ to represent the process visually!
✅ Keep your answer concise yet detailed to score well.
Back Excercise Questions – Answers
Q. 1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer:-
🌱🦠 Comparison: Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
📊 Table: Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
| Feature 🏷️ | Plant Cells 🌱 | Animal Cells 🦠 |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall 🏗️ | ✅ Present (made of cellulose) | ❌ Absent |
| Shape 🔷 | Generally rectangular | Usually round or irregular |
| Chloroplasts 🌞 | ✅ Present (for photosynthesis) | ❌ Absent |
| Vacuole 💧 | Large central vacuole | Small or absent vacuoles |
| Centrioles 🔄 | ❌ Absent | ✅ Present (helps in cell division) |
| Mode of Nutrition 🍽️ | Autotrophic (prepares own food) | Heterotrophic (depends on other organisms) |
| Lysosomes ☠️ | Rarely found | ✅ Present (helps in digestion) |
🔹 💡 Key Takeaways:
✔ Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large vacuole for storing water. 🌿
✔ Animal cells lack a cell wall, lack chloroplasts, and have centrioles for cell division. 🧬
✔ Plant cells carry out photosynthesis, while animal cells depend on consuming food. 🍎
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Use a clear diagram 🖼️ comparing plant and animal cells.
✅ Mention examples like leaf cells (plants) and muscle cells (animals). 🌱🐾
✅ Highlight key differences in cell structure with headings for clarity. 📌
✅ Keep the answer neat, structured, and well-explained to score full marks! ✅📚
Q. 2. How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer:-
🦠 Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Here’s a structured comparison to help you ace your board exams! 🚀📚
📊 Table: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
| Feature 🏷️ | Prokaryotic Cells 🦠 | Eukaryotic Cells 🧬 |
|---|---|---|
| Size 📏 | Small (1-10 µm) | Larger (10-100 µm) |
| Nucleus 🎯 | ❌ No true nucleus (nucleoid present) | ✅ Well-defined nucleus with a nuclear membrane |
| DNA Structure 🧬 | Circular, single chromosome | Linear, multiple chromosomes |
| Membrane-bound Organelles 🏭 | ❌ Absent | ✅ Present (e.g., mitochondria, Golgi body, ER) |
| Cell Division ✂ | Binary fission (simple division) | Mitosis & meiosis (complex division) |
| Examples 🔍 | Bacteria, archaea | Plants, animals, fungi, protists |
🔹 💡 Key Takeaways:
✔ Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are complex and have membrane-bound organelles. 🔬
✔ Prokaryotes reproduce by binary fission, whereas eukaryotes use mitosis & meiosis. ✂
✔ Examples: Bacteria (prokaryotes) vs. plant and animal cells (eukaryotes). 🌱🐾
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Draw a neat diagram 🖼️ comparing both cell types.
✅ Highlight nucleus & organelles as key distinguishing features. 🎯
✅ Keep answers structured with headings for clarity and full marks! ✅📚
Q. 3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer:-
🩸 What Happens If the Plasma Membrane Ruptures or Breaks Down?
🔹 🔬 Importance of the Plasma Membrane:
The plasma membrane (also called the cell membrane) is a selectively permeable layer that protects the cell and regulates the entry and exit of substances. 🚪✨
🔹 ⚠ Consequences of Rupturing the Plasma Membrane:
✅ Loss of Selective Permeability 🔄 – The cell can no longer control what enters or exits, leading to an imbalance of ions, nutrients, and water.
✅ Leakage of Cytoplasmic Contents 💧 – The cytoplasm spills out, affecting vital cellular functions.
✅ Disruption of Cellular Activities ⚙ – Organelles like mitochondria and ribosomes fail to function properly, stopping respiration and protein synthesis.
✅ Cell Death ☠️ – If the damage is severe, the cell cannot survive, leading to its destruction.
🔹 💡 Reasons for Membrane Rupture:
❌ Mechanical Injury – Physical damage like crushing or tearing can break the membrane.
❌ Chemical Exposure – Harmful substances like strong acids or toxins may weaken the membrane.
❌ Extreme Temperature – Very high or low temperatures can damage the lipid bilayer.
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Define plasma membrane and highlight its protective function.
✅ Explain why cell survival depends on membrane integrity.
✅ Draw a diagram 🖼️ showing cell rupture for better understanding.
✅ Keep your answer structured and precise for full marks! ✅📚
Q. 4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer:-
📦 What Would Happen to a Cell Without the Golgi Apparatus?
🔹 🔬 Role of the Golgi Apparatus:
The Golgi apparatus is like the “packaging and distribution center” of the cell. It helps in modifying, sorting, and transporting proteins and lipids to their appropriate destinations. 🚚✨
🔹 🚨 Consequences of Losing the Golgi Apparatus:
✅ Incomplete Protein Processing ⚙️ – Proteins produced by the ribosomes would remain unmodified, making them ineffective.
✅ Disrupted Transport System 📦 – The cell would struggle to send proteins and enzymes to the right locations.
✅ Failure in Secretion 🔄 – Important substances like hormones, enzymes, and mucus wouldn’t be properly released.
✅ Accumulation of Unprocessed Materials 🚧 – Waste and unprocessed molecules would build up inside the cell, leading to dysfunction.
✅ Cellular Breakdown & Death ☠️ – Over time, the cell would not function properly and may eventually die due to lack of coordination.
🔹 💡 Why Is the Golgi Apparatus Essential?
✔ It ensures proper transport and delivery of proteins. 🚀
✔ Helps in forming lysosomes, which digest unwanted materials. 🦠
✔ Maintains cell balance by sorting and packaging molecules. 📦
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Explain Golgi’s role in protein modification and transport clearly.
✅ Highlight how the absence of Golgi affects different cellular functions.
✅ Use a neat diagram 🖼️ of the Golgi apparatus for better marks!
✅ Keep your answer structured and well-explained to maximize your score. ✅📚
Q. 5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer:-
⚡ Which Organelle is Known as the Powerhouse of the Cell?
🔹 Mitochondria: The Powerhouse of the Cell 🏭
Mitochondria are called the “powerhouse of the cell” because they generate energy (ATP) needed for various cellular activities. They play a crucial role in cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down to release energy. 🔥
🔹 🔬 Why Are Mitochondria So Important?
✅ ATP Production: Mitochondria convert nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the cell. 💡
✅ Double Membrane Structure: Their inner membrane has folds called cristae, which increase the surface area for energy production. 🏗️
✅ Contains Its Own DNA: Mitochondria have their own genetic material, allowing them to replicate independently. 🧬
🔹 🌀 Process of Energy Production:
1️⃣ Glycolysis – Breakdown of glucose outside the mitochondria. 🍞➡️⚡
2️⃣ Krebs Cycle – Further breakdown in the mitochondrial matrix. 🔄
3️⃣ Electron Transport Chain – Major ATP synthesis occurs here. 🚀
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Clearly mention ATP production as the main function.
✅ Explain mitochondrial structure with key terms like cristae and double membrane. 🏗️
✅ Draw a simple diagram of mitochondria 🖼️ to enhance your answer.
✅ Keep your explanation concise but well-detailed to score full marks! 📚
Q. 6. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer:-
🧪 Where Are the Lipids and Proteins Constituting the Cell Membrane Synthesized?
🔹 🔬 Lipid Synthesis: Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
✅ Lipids, the essential components of the plasma membrane, are synthesized in the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). 🏗️
✅ The SER helps in the formation of phospholipids, which are crucial for membrane fluidity and structure. 🌊
🔹 ⚙ Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes & Rough ER
✅ Proteins needed for the plasma membrane are synthesized by ribosomes, the “protein factories” of the cell. 🏭
✅ Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) processes these proteins and transports them for incorporation into the membrane. 🚀
🔹 🔄 Modification & Transport: Golgi Apparatus
✅ The Golgi body further modifies and packages proteins and lipids into vesicles for transport to the cell membrane. 📦
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Clearly mention SER for lipids and RER + ribosomes for proteins.
✅ Highlight Golgi body’s role in processing & transport. 🚛
✅ Draw a simple diagram 🖼️ illustrating lipid and protein synthesis pathways.
✅ Keep the explanation concise, structured, and well-explained for full marks! 📚✅
Q. 7. How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer:-
🦠 How Does an Amoeba Obtain Its Food?
Amoeba is a unicellular organism that feeds through a special process called phagocytosis. Let’s break it down step by step! 🚀
🔹 1. Detection of Food 🔍
- Amoeba senses its food, such as bacteria or microscopic organisms, in its surrounding water. 🌊
🔹 2. Formation of Pseudopodia ✋
- It extends finger-like projections called pseudopodia (meaning “false feet”) around the food particle. 🏗️
- The food gets enclosed within these pseudopodia, forming a food vacuole.
🔹 3. Digestion Inside Food Vacuole 🍽️
- Enzymes from the cytoplasm break down the food inside the food vacuole. 🧪
- The nutrients are absorbed into the cytoplasm, providing energy to the Amoeba. ⚡
🔹 4. Excretion of Waste 🚮
- After digestion, the undigested food is expelled out of the cell through the cell membrane. 🚪
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Use a labeled diagram 🖼️ of Amoeba engulfing food.
✅ Highlight pseudopodia and food vacuole formation as key points. ✍️
✅ Keep the answer well-structured, concise, and scientifically accurate. 📚✅
✅ Mention phagocytosis as the main process! 🚀
Q. 8. What is osmosis?
Answer:-
💧 Osmosis: The Special Type of Diffusion
🔹 🔬 Definition:
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. 🌊✨
🔹 ⚙ Importance of Osmosis:
✅ Maintains water balance in cells. ⚖️
✅ Helps in the absorption of nutrients in plants. 🌱
✅ Plays a crucial role in exchange of fluids in organisms. 🧬
🔹 🌀 Types of Solutions Affecting Osmosis:
1️⃣ Hypotonic Solution 💦 – Higher water concentration outside the cell → Water moves inside → Cell swells. 🏡📈
2️⃣ Hypertonic Solution 🔥 – Higher water concentration inside → Water moves out → Cell shrinks. 📉
3️⃣ Isotonic Solution ⚖️ – Equal water concentration → No net movement → Cell stays normal. ✅
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Always define osmosis clearly and mention the selectively permeable membrane.
✅ Include real-life examples like plant root absorption and RBC shrinkage in saline water. 🌱🩸
✅ Use a neat diagram 🖼️ showing water movement in different solutions.
✅ Keep your answer concise but well-explained to score full marks! 📚✅
Q. 9. Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoos each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough
containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D. Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D.
Answer:-
🔬 Osmosis Experiment Using Potato Cups
📌 Observation & Explanation:
(i) Why does water gather in the hollowed portion of B and C?
✅ Sugar in cup B and salt in cup C create a hypertonic solution, meaning the concentration of solutes inside the cups is higher than outside. 🏗️
✅ Due to osmosis, water from the surrounding moves into the hollowed portions to balance the concentration. 💧➡️🥔
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
✅ Potato A serves as a control to compare changes caused by osmosis. 🎯
✅ Since it is empty, there is no concentration difference, preventing water movement. 🌊❌
(iii) Why does water not gather in the hollowed portions of A and D?
✅ In cup A, there is no solute to create a concentration difference, so osmosis does not occur. 🚫💧
✅ In cup D, the potato is boiled, damaging its cell membranes, making it unable to perform osmosis effectively. 🔥🥔➡️❌
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Define osmosis clearly with mention of selectively permeable membranes. 🔬
✅ Explain hypertonic solutions and why they cause water movement. 💧📈
✅ Draw a neat diagram 🖼️ illustrating the experiment for better clarity.
✅ Keep the answer concise, structured, and well-explained for full marks! ✅📚
Q. 10. Which type of cell division is required for growth and repair of body and which type is involved in formation of gametes?
Answer:-
🧬 Types of Cell Division: Growth vs. Gamete Formation
Cell division is essential for the survival of organisms, and it occurs in two major forms: Mitosis and Meiosis. Let’s break them down for clarity! 🚀
🔹 1. Mitosis – For Growth & Repair 🏗️
✅ Mitosis helps in the growth, repair, and replacement of damaged cells.
✅ It occurs in somatic cells (body cells).
✅ Produces two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
✅ Example: Healing of wounds, growth of tissues, replacement of old cells. 🌱✨
🔹 2. Meiosis – For Gamete Formation 🔄
✅ Meiosis is responsible for the production of gametes (sperm & egg) in sexually reproducing organisms.
✅ Occurs in reproductive cells (gonads).
✅ Produces four daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes (haploid).
✅ Ensures genetic variation among offspring. 🧬
💡 ✨ Exam Tips:
✅ Clearly differentiate mitosis for growth/repair and meiosis for gamete formation.
✅ Mention chromosome number differences (diploid vs. haploid).
✅ Use a neat diagram 🖼️ of both processes for better clarity.
✅ Keep answers structured and well-explained to score full marks! 📚✅